Android Basics : Quick Start
First of all, basic question: How to learn Android?
Ok. Lets continue...
There are 4 basic components in Android application.
1. Activity
2. View
3. Service
Readings:
[1] http://www.androidcompetencycenter.com/2009/01/basics-of-android-part-iii-android-services/
[2] http://mylifewithandroid.blogspot.com/2008/02/double-life-of-service.html
4. Intent
Hope this article help those who just started in Android Development. :)
Read more at http://developer.android.com/guide/index.html.
- “Google” it. (Sorry for the foul language =p)
- API & book references.
- Ask experienced people.
- Think yourself.
- Ask in forum or send email.
Ok. Lets continue...
There are 4 basic components in Android application.
 |
| Activity Life-cycle |
- Displays a user interface component and respond to system/user initiated.
- An Application may contain one or more Activities. One Activity is then considered as the main entry point by the system.
- Each Activity can be invoked from other Applications/Activities.
- Example:
public class Activity extends ApplicationContext {
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedState);
protected void onStart();
protected void onRestart();
protected void onResume();
protected void onPause();
protected void onStop();
protected void onDestroy();
}
public class MyActivity extends Activity {}
 |
| Different Layout View |
- The basic building block for user interface components and creation of interactive UI components (buttons, text fields, etc.).
- Occupies a rectangular area on the screen and is responsible for drawing and event handling (scroll, tap, etc.).
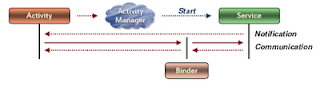
3. Service
- An application component that runs in the background, not interacting with the user, for an indefinite period of time.
- Two modes: a long-running service whose lifecycle is independent of the activity that started it; a service bound by other services and activities by its AIDL interface.
- Example:
public class MyService extends Service {
public void onCreate();
public void onDestroy();
private final IService.Stub mBinder = new IService.Stub() {
//your service methods implementation
Method1();
Method2();
}
public IBinder onBind(Intent arg0) {
return mBinder;
}
}
Readings:
[1] http://www.androidcompetencycenter.com/2009/01/basics-of-android-part-iii-android-services/
[2] http://mylifewithandroid.blogspot.com/2008/02/double-life-of-service.html
4. Intent
- An intent is an abstract description of an operation to be performed.
- Its most significant use is in the launching of Activities, where it can be thought of as the glue between Activities.
- It is a passive data structure holding an abstract description of an action to be performed.
- action
- data
- Usage
- Explicit passing: startActivity(Intent); startService(Intent)
- Broadcast: broadcastIntent – need to declare Intent Filter to receive the event.
Hope this article help those who just started in Android Development. :)
Read more at http://developer.android.com/guide/index.html.


Comments
Post a Comment